|
7. DARK MATTER
7.1 Historical Introduction
- Dark matter in the Galactic disk (Oort)
- Dark matter in the Coma cluster (Zwicky)
- Stability of cold disks versus bars (Ostriker &Peebles)
7.2 Observational Evidence for Dark Matter
- HI rotation curves
- Velocity dispersions in dSph galaxies
- Satellites of our Galaxy
- X-ray gas in galaxies and clusters: hydrostatic equilibrium of a hot gas
- Velocity dispersions of clusters of galaxies
- Gravitational lenses
- Large-scale velocity fields
7.3 Regularities in DM Halo Properties
- Conspiracy between luminous and dark matter to make flat V (r )
- Parameter correlations
- Rotation curve decomposition into visible and dark matter components
- Fundamental plane for dark matter halos
- Evidence for baryonic compression of dark matter halos
- Implications for galaxy formation
7.4 What is Dark Matter?
- MOND: Modified Newtonian Dynamics?
- Disk dark matter is baryonic: it dissipated
- Primordial nucleosynthesis constraints on baryonic dark matter
- Baryonic halos?
- Things that won’t work: snowballs, M dwarfs, white dwarfs, neutron stars
- Things that might work: brown dwarfs, black holes of mass 105±1
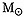
- Gravitational microlensing surveys
- Hot, warm, and cold elementary particles
- Constraints on neutrino dark matter from dwarf galaxies
- Direct detection of particle dark matter
|