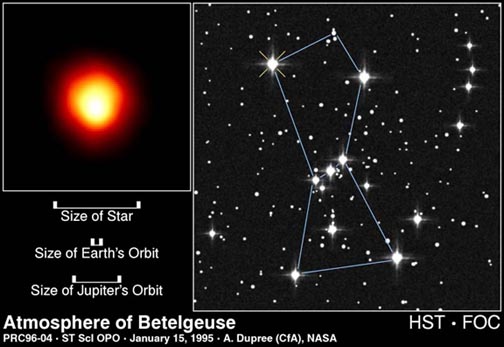
Betelgeuse is found in the constellation
Orion. If you can't find Orion in the sky, try searching
the web using keywords Betelgeuse or Orion.
Two of the many good sources of information on what to look for
in the night sky are: Skywatch
and Heavens
Above.
From Sciencenet:
The Hunter's right shoulder is marked by the brilliant orange
star Betelgeuse lying 457 light-years from Earth. This huge red
supergiant is one of the largest stars known; if it were to take
the place of the Sun in our solar system its gigantic diameter
would extend beyond the orbit of Mars. Betelgeuse is entering
the twilight years of its life and has cooled considerably since
is youth hence its orange huge. The colour of stars are related
to their age. Young stars generate more energy and are hotter
shining brightly with a blue or white light. As they grow old
the energy they produce dwindles and their temperature drops;
the dominant light emitted then turns from white to yellow though
to orange and finally red, much like the dying embers of a coal
fire. The surface temperature of Betelgeuse is cooler than the
Sun measuring approximately 3000°C compared with 6000°C.
This is what Betelgeuse looks like to the
HST: